8.1 INTRODUCTION
A sequential circuit consists of memory elements, such as flip-flops and combinational logic circuits Figure 8.1 shows the basic block diagram of a sequential circuit. The sequential circuit is a feedback system as the present state of the_ circuit is fad back to the input decoder and is used determine the next state of the machine.
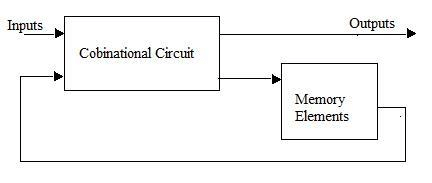
Basic block diagram of sequential circuit 👆👆👆👆👆
The next state of the LA Outputs machine can be determined by the present state of the circuit and inputs. The input decoder performs the logic operations based on the present state of the circuit and inputs and generates Basic block diagram of sequential circuit next state code of the circuit Then the next state code is stored in the memory, in sequential circuit, the output depends on the im- mediate input to the circuit and also the present state of the circuit. The present state of the circuit is also stored in the memory element.
There are two types of sequential circuits, such as synchronous sequential circuit and asynchronous sequential circuit. In synchronous sequential circuit, state changes are synchronized to the periodic clock pulses, but state changes of asynchronous sequential circuit are not synchronized with clock signal. Most commonly used sequential circuits are registers and counters. In this chapter, operating principles and applications of registers and counters are discussed in-detail
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
- REGISTER
- SHIFT REGISTER
- CLASSIFICATION OF SHIFT REGISTER
- SERIAL IN-PARALLEL OUT (SIPO) SHIFT REGISTERS
- SERIAL IN-SERIAL OUT(SISO) SHIFT REGISTERS
- PARALLEL IN-SERIAL OUT (PISO) SHIFT REGISTERS
- PARALLEL IN-PARALLEL OUT (PIPO) SHIFT REGISTERS
- UNIDIRECTIONAL SHIFT REGISTERS
- LEFT SHIFT REGISTERS
- RIGHT SHIFT REGISTERS
- BI-DIRECTIONAL SHIFT REGISTERS
- SERIAL IN-PARALLEL OUT (SIPO) SHIFT REGISTERS = (a) – 4-bit sipo shift register using d flip-flop (b) – sipo shift register using j-k flip-flop
- SERIAL IN -SERIAL OUT SHIFT REGISTERS
- PARALLEL IN-PARALLELOUT SHIFT REGISTERS
- PARALLEL IN-SERIAL OUT SHIFT REGISTER
- BUFFER REGISTER
- UNIVERSAL SHIFT REGISTER
- UNIVARSAL SHIFT REGISTER USING MUX
- APPLICATIONS OF SHIFT REGISTERS
- TIME DELAY
- SHIFT REGISTER COUNTERS
- SERIAL DATA TO PARALLEL DATA CONVERSION
- COUNTER
- CLASSIFICATION OF COUNTER
- ASYNCHORONOUS (RIPPLE) COUNTER = (a) 1 bit ripple counter (b) 2-bit ripple up counter (c) 2-bit ripple down counter (d) 3-bit ripple up counter (e) 3-bit ripple down counter (f) 4-bit ripple up counter (g) 4-bit ripple down counter
- ASYNCHORONOUS DECADE COUNTERS
